CSCI 4320 (Principles of Operating Systems), Fall 2005:
Homework 6
- Assigned:
- December 2, 2005.
- Due:
- December 9, 2005, at 5pm.
Not accepted late.
- Credit:
- 20 points.
Be sure you have read Chapter 6.
Answer the following questions. You may write out your answers by
hand or using a word processor or other program, but please submit
hard copy, either in class or in my mailbox in the department office.
- (5 points)
Consider a simple operating system that provides
only a single-level directory, but allows the directory
to contain as many files as desired, with file names as
long as desired. Would it be possible to use this
system to simulate
something resembling a hierarchical file system? How?
- (5 points)
Consider a digital camera that records photographs
in some non-volatile storage medium (e.g., flash memory).
Photographs are recorded in sequence until the medium
is full; at that point, the photographs are transferred
to a hard disk and the camera's storage is cleared.
If you were implementing a file system for the camera's
storage, what strategy would you use for file allocation
(contiguous, linked-list, etc.) and why?
Notice that this camera does not have the ability to
delete photographs from its storage one at a time,
so your file system does not need to support that.
- (5 points)
The textbook describes two strategies
for keeping track of free blocks in a file system,
one using a list of free blocks and one using a bitmap.
What would happen if this free list or bitmap was completely
lost because of a system crash -- is there a way to
recover/rebuild the list or bitmap,
or do you have to just reformat the disk and hope you
backed up any really important files?
Answer separately for UNIX V7 and MS-DOS FAT-16 filesystems.
(Hint: Read the last paragraph of section 6.4.3
carefully.)
- (5 points)
Consider a UNIX filesystem (as described in section
6.4.5) in which each i-node contains
10 direct entries, one single-direct entry,
one double-indirect entry, and
one triple-indirect entry. If a block is 1KB (1024 bytes)
and a disk addresses is 4 bytes, what is the maximum file
size, in KB?
(Hint: Use the blocksize and size of disk addresses
to determine how many entries each indirect block contain.)
(Optional)
Do the following programming problems. You will end up with at
least one code file per problem.
Submit your program source (and any other needed files)
by sending mail to
bmassing@cs.trinity.edu,
with each file as an attachment.
Please use a subject line that mentions the course number and
the assignment (e.g., ``csci 4320 homework 6'').
You can develop your programs on any system that provides the
needed functionality, but I will test them on one of the department's
Fedora Core 4 Linux machines, so you should probably make sure they work
in that environment before turning them in.
- (Up to 5 extra-credit points)
Write a program that given a directory
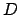 , blocksize
, blocksize 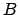 ,
and maximum number of blocks
,
and maximum number of blocks 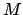 as command-line arguments
prints out how many files in
as command-line arguments
prints out how many files in 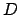 and its subdirectories
are of size
and its subdirectories
are of size 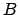 or less, how many are of size between
or less, how many are of size between 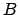 and
and 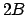 ,
etc., up to size
,
etc., up to size 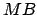 .
Include directories and symbolic links (but count the size of the link
and not the file/directory it links to).
Here is a sample execution.
.
Include directories and symbolic links (but count the size of the link
and not the file/directory it links to).
Here is a sample execution.
[bmassing@Xena02]$ ./filesizes /var/www 512 20
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/howland-cousins/config: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/About/The_Courses/cs3394.hci/dcernose/javapres/turnin/COM: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/About/The_Courses/cs3291.java/dcernose/javapres/turnin/COM: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/cs1300/config: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/apache-documentation/manual/search: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/TUSSW/config: Permission denied
Unable to open /var/www/HTML-Documents/TUSSW/magpierss-0.61: Permission denied
Results for directory /var/www:
2870 files of size 1 blocks
833 files of size 2 blocks
1231 files of size 3 blocks
1310 files of size 4 blocks
7300 files of size 5 blocks
9882 files of size 6 blocks
5870 files of size 7 blocks
3888 files of size 8 blocks
1847 files of size 9 blocks
1049 files of size 10 blocks
1663 files of size 11 blocks
745 files of size 12 blocks
469 files of size 13 blocks
697 files of size 14 blocks
554 files of size 15 blocks
545 files of size 16 blocks
469 files of size 17 blocks
322 files of size 18 blocks
345 files of size 19 blocks
291 files of size 20 blocks
6917 files of size 21 blocks or more
(Of course, you won't be able to examine files in directories you
don't have access to. That's okay; just print error messages as above.)
Hints: Read the man pages for
opendir, readdir, and lstat.
You might also be interested in the man pages for
chdir and strerror.
Berna Massingill
2005-12-02