Curve Deform
by Kenneth Styrberg
Relevant to Blender v2.35
Introduction
Curve Deform provide a simple but efficient method to define a deformation on a mesh. By parenting a mesh object to a curve, you can deform the mesh along the curve by moving the mesh along, or orthogonal to, the dominant axis.
The Curve Deform work on a dominant axis, X, Y, or Z. This means that when you move your mesh in the dominant direction, the mesh will traverse along the curve. Moving the mesh in an orthogonal direction will move the mesh object closer or further away from the curve. The default settings in Blender map the Y axis to the dominant axis. When you move the object beyond the curve endings the object will continue to deform based on the direction vector of the curve endings.
 | Try to position your object over the curve while moving it around. This gives the best control over how the deformation work. |
Interface
When parenting a mesh to a curve (CTRL-P), you will be presented with a menu, Figure 37. By selecting Curve Deform you have enable the Curve Deform function on the mesh object.
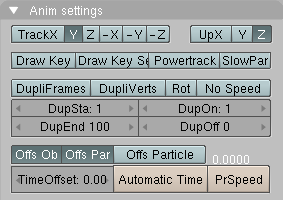
The dominant axis setting is set on the mesh object. By default the dominant axis in Blender is Y. This can be changed by selecting one of the Track X,Y or Z buttons in Anim Panel, Figure 38, in Object Context (F7).
Cyclic curves work as expected, where the object deformation traverse along the path in cycles.
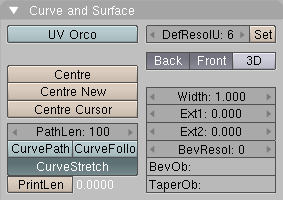
CurveStretch gives an option to let the mesh object stretch , or squeeze, over the entire curve. This option is in Edit Context (F9) for the curve. See Figure 39.
Example
Lets make a simple example.
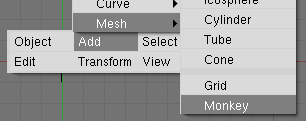
1. Remove default cube object from scene and add a Monkey! (SHIFT-A -> Add -> Mesh -> Monkey, Figure 40)
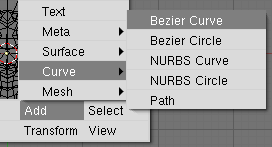
2. Now press TAB to exit Edit Mode. Now add a curve. (SHIFT-A -> Add -> Curve -> Bezier Curve, Figure 41)
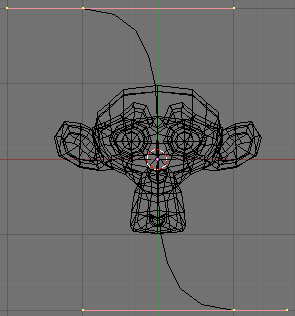
3. While in editmode, move the control points of the curve as Figure 42, then exit Edit Mode, (TAB).
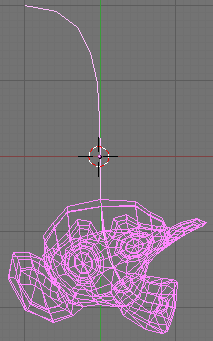
4. Select the Monkey, (RMB), and then shift select the curve, (SHIFT-RMB). Press CTRL-P to open up the Make Parent menu. Select Curve Deform. Figure 37 in the Section called Interface.
The Monkey should be positioned on the curve as Figure 43.
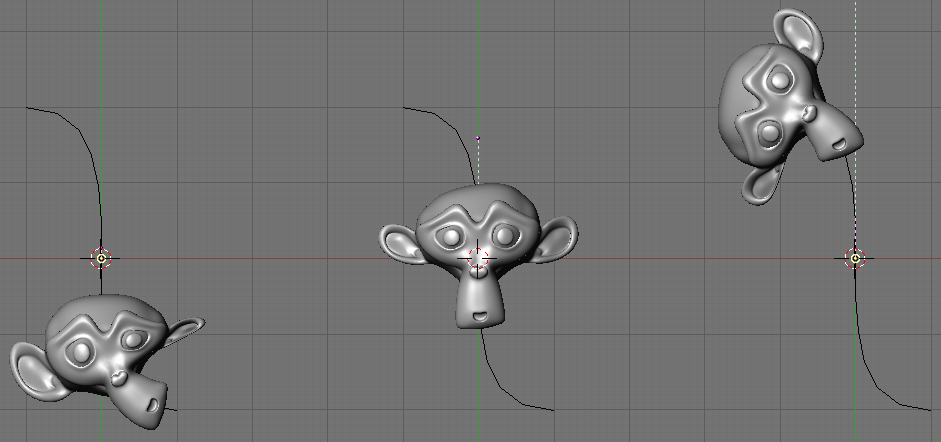
5. Now if you select the Monkey, (RMB), and move it, (G), in the Y-direction, (the dominant axis by default), the Monkey will deform nicely along the curve.
 | If you press MMB while moving the Monkey you will constrain the movement to one axis only. |
6. In Figure 44, you can see the Monkey at different positions along the curve. To get a cleaner view over the deformation I have activated SubSurf with Subdiv 2 and Set Smooth on the Monkey mesh. (F9 to get Edit options).
 | Moving the Monkey in other directions than the dominant, will create some odd deformations. Sometime this is what you want to achieve so you'll need to experiment and try it out! |